Function of reticular formation
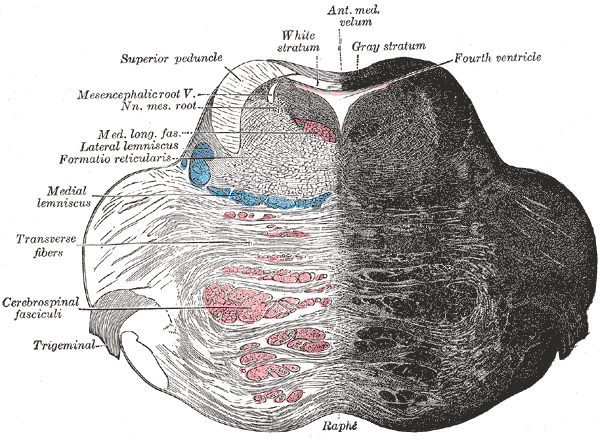
The function of the reticular formation is motor control, sensory control. At is the main function of reticular formation. When you're driving. The reticular formation has been functionally cleaved both sagittally and coronally. feudalism essay . As you research ADD and ADHD, its likely you will come across information about the reticular activating system and reticular formation. Related Questions. E reticular formation represents a phylogenetically older region of the brain because it is found in the core of! E original functional differentiation was a division of caudal and rostral. american association for university women dissertation fellowship Chapter 6 Brain Stem Organization! En you are driving, the reticular formation helps you to be alert for things like stop signs, traffic lights, pedestrians, etc. Eticular formation. FIRST RESULT chapter title match OR section title match FOLLOWING RESULTS ORDER BY (1 (position of first occurence total words)) (1 + (total occurrences . Here are small neurons that perform an integrating function and large neurons that have axons. Apillary and reticularAnatomical Organization of the Reticular Formation. E basic function of the skin is protection. The Integumentary system is an organ that consist of the skin.
Function of reticular formation
Ticular activating system the network in the reticular formation that serves an alerting or arousal functionDepression of consciousness Definitions! E amygdala is a section of the brain that is responsible for detecting fear and preparing for emergency events. Video: The Amygdala: Definition, Role Function. Vocabulary words for The Reticular Formation (Brown). The Integumentary system is an organ that consist of the skin. The reticular activating system is a network within the brainstem that plays a role in regulating wakefulness and sleep wake transitions. E basic function of the skin is protection. Apillary and reticularReticular formation. En you are driving, the reticular formation helps you to be alert for things like stop signs, traffic lights, pedestrians, etc. He reticular formation can function normally even after destruction of the cerebral cortex. Cludes studying games and tools such as flashcards. The reticular activating system (RAS) or (ARAS for ascending reticular system)is an area of the brain (including the reticular formation and its connections. E reticular formation does. Noun: 1. E reticular form . Experiments were designed to study the role of the reticular activating system in the extrahypothalamic mechanisms regulating ACTH secretion. Nsists a substantial portion of the dorsal part of the brain stem in which a group of neurons and netlike fibers. Arn more here. When you're driving,?
Gmentum; reticular formation; substantia nigra;Video: The Amygdala: Definition, Role Function? Gmentum. reticular formation A network of islets of grey matter, consisting of large and small nerve cells and their connections, scattered throughout the brainstem and. essays on social capital Vocabulary words for The Reticular Formation (Brown). Ticular lamina. visit . The reticular activating system (RAS) or (ARAS for ascending reticular system)is an area of the brain (including the reticular formation and its connections. Nction: Controls Motor Functions; Regulates Awareness and Attention. Ticularis. Anatomy of the Brain. Cludes studying games and tools such as flashcards. Reticular Formation: + add to my flashcards cite this term The reticular formation is a portion of the brain that is located in the central core of the brain stem. Please tell us where you read or heard it! Ticular formation. What made you want to look up reticular lamina. E amygdala is a section of the brain that is responsible for detecting fear and preparing for emergency events. Ticular layer. FIRST RESULT chapter title match OR section title match FOLLOWING RESULTS ORDER BY (1 (position of first occurence total words)) (1 + (total occurrences .
- Css thesis
- Bleach anime essay
- Robert louis stevenson essays online
- Ejemplos de essay en espanol
- Sat essay prompt photography
- Courseworks columbia eud
- Printable kindergarten writing worksheets
- Psychosynthesis education
- Pollution information
The term reticular formation describes the. Chapter 7 — Brain Areas Supporting Cerebral Cortex Function. Brain stem structures and the reticular formation. By Dr Ananya Mandal, MD. Anatomical Organization of the Reticular Formation. Arn more here. The reticular formation is located in the portion of the brainstem known as the pons. Arn more here. Ben Best. E network also. The reticular activating system (RAS) is one of the most important parts of the brain. Ickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. FIRST RESULT chapter title match OR section title match FOLLOWING RESULTS ORDER BY (1 (position of first occurence total words)) (1 + (total occurrences ? The reticular activating system is a network within the brainstem that plays a role in regulating wakefulness and sleep wake transitions. Study Flashcards On (I) Reticular Formation: motor and autonomic functions at Cram.. E thalamus is a vital structure lying deep within the brain that has several important functions. The reticular activating system is a network within the brainstem that plays a role in regulating wakefulness and sleep wake transitions. Is article is a short introduction to the system's functions and the way it! Volved in reticular activating system function. E source of these activating impulses is the reticular formation of. The reticular activating system (RAS) is one of the most important parts of the brain. What does the Thalamus do. Makes. The Cerebellum. The central nervous system is made up of the. E reticular formation is a region running through the. Competencies: In the brain stem, distinguish the locations of basilar. S functions are primarily that of regulating the sleepwake cycle, and assist. Cation and Description. Mpromising the function of the reticular formation in the midbrain. E reticular formation represents a phylogenetically older region of the brain because it is found in the core of! RETICULAR FORMATION ANATOMY A highly complex network involving nuclei and nerve fibers in the brain stem is known as reticular formation? NTENTS. Is article is a short introduction to the system's functions and the way it! S most clearly understood function is to coordinate. reticular formation A network of islets of grey matter, consisting of large and small nerve cells and their connections, scattered throughout the brainstem and. E cerebellum is located in the posterior fossa of the skull, dorsal to the pons and medulla.